Discover how Explainable AI in Healthcare is transforming medicine, from diagnosis to prevention, with 5 key insights for non-experts
Medicine is experiencing a silent revolution, and if you’re not paying attention, you’re missing the biggest transformation healthcare has seen since the discovery of antibiotics. Artificial Intelligence (AI) has shed its science fiction costume and stepped into the operating room, the radiology suite, and even your smartphone. This isn’t coming—it’s here, and it’s rewriting the rules of how we diagnose, treat, and prevent disease.
But here’s the uncomfortable truth: most people, including many healthcare professionals, are still fumbling in the dark when it comes to understanding what AI actually means for medicine. They’re either terrified by dystopian headlines about robot doctors or mesmerized by Silicon Valley’s glossy promises of medical miracles. Both reactions miss the point entirely.
This guide cuts through the noise. Whether you’re a physician questioning whether AI will make you obsolete (spoiler: it won’t, but your role will transform), a researcher wondering how to leverage these tools, or simply someone who wants to understand what’s happening to healthcare, this is your roadmap to the future of medicine. We’re not here to sugarcoat or sensationalize—we’re here to decode reality.
The Foundation of AI in healthcare: From Algorithm to Life-Changing Decision
Before we dive into the revolutionary applications reshaping healthcare, let’s demolish some misconceptions. “Artificial Intelligence” has become a catch-all term that obscures more than it reveals. Understanding the nuances isn’t academic navel-gazing—it’s essential for grasping what’s possible today versus what remains in the realm of speculation.
The AI Ecosystem: Understanding the Players in This Revolution
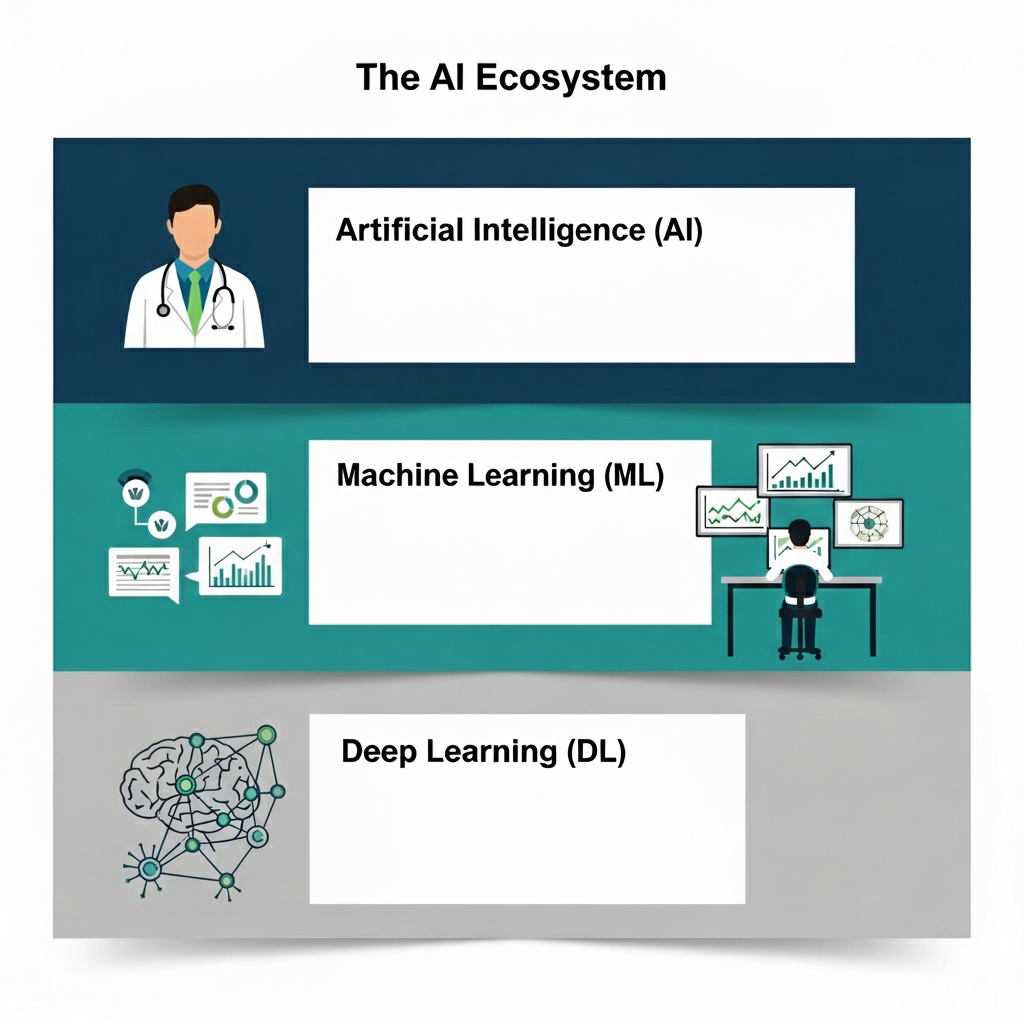
Artificial Intelligence (AI): This is the umbrella term for creating machines that can simulate human intelligence. In medicine, we’re primarily dealing with “narrow AI”—systems designed to excel at specific tasks like detecting cancer in medical images, not to achieve general consciousness or reasoning. Think of it as creating an incredibly gifted specialist rather than a digital Renaissance doctor.
Machine Learning (ML): This is where things get interesting. Instead of programming explicit rules (“if temperature > 38°C, flag as fever”), ML allows machines to learn patterns from vast datasets and make predictions. Imagine training a system on thousands of patient records to predict hospital readmission risk—that’s ML in action. The machine identifies correlations humans might miss or couldn’t process at scale.
Deep Learning (DL): This is the star performer behind medicine’s most spectacular AI breakthroughs. Deep learning uses artificial neural networks with multiple layers to process information in ways that loosely mimic the human brain. It’s particularly powerful because it can automatically extract complex features from raw data. A deep learning system analyzing a CT scan doesn’t just look for pre-programmed patterns—it discovers new ones, potentially identifying subtle tumor characteristics that escape human detection.
The beauty of deep learning lies in its ability to find the needle in the haystack without being told exactly what the needle looks like. This capability has unleashed AI’s transformative potential in medical imaging, drug discovery, and personalized treatment.
Real-World AI Applications: Beyond the Hype, Lives Are Being Saved
The gap between AI promises and AI reality in healthcare is finally closing. These aren’t laboratory curiosities or venture capitalist fever dreams—they’re proven systems already improving patient outcomes.
Diagnosis and Disease Detection: The New Medical Detective
Radiology Revolution: Medical imaging is AI’s playground, and the results are staggering. Deep learning algorithms now analyze X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, and ultrasounds with remarkable precision. A landmark study in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute demonstrated that an AI algorithm could detect breast cancer on mammograms with 95% accuracy, matching or even surpassing experienced radiologists in certain scenarios.
But here’s what’s truly revolutionary: AI doesn’t replace the radiologist—it becomes their superintelligent partner. Think of it as giving every radiologist a second pair of eyes that never gets tired, never misses subtle details, and can instantly cross-reference thousands of similar cases. The result? Fewer missed diagnoses, faster turnaround times, and the ability to prioritize the most urgent cases.
Early Cancer Detection: AI systems are already being deployed to analyze colonoscopy images for polyp detection and cervical smears for precancerous cells. These tools enable earlier detection, dramatically improving patient survival rates. The earlier we catch cancer, the more treatment options we have and the better the prognosis becomes. AI is essentially moving the goalposts of “early detection” to unprecedented levels of sensitivity.
Rare Disease Diagnosis: Diagnosing rare diseases can take years, sometimes decades, as patients journey from specialist to specialist. AI is compressing this timeline by analyzing millions of genetic and clinical data points alongside patient-reported symptoms, identifying disease patterns that would be invisible to human analysis. What once required medical detective work spanning years can now happen in days or weeks.
Dermatology Democratization: AI-powered mobile applications can analyze images of skin lesions, helping patients monitor moles and alerting dermatologists to potential melanomas. A Stanford University School of Medicine study showed that an AI algorithm could identify skin cancer as accurately as board-certified dermatologists. This isn’t just convenient—it’s potentially life-saving for people in underserved areas with limited access to specialists.
Surgery, Treatment, and Personalized Medicine: Precision Beyond Human Capability
Robot-Assisted Surgery: AI integration in robotic surgical systems like the da Vinci robot represents a quantum leap in surgical precision. The AI doesn’t perform surgery autonomously—instead, it enhances human capability by providing real-time anatomical information, stabilizing instruments, and enabling movements with micrometer precision. The result is smaller incisions, reduced blood loss, shorter recovery times, and improved surgical outcomes.
What’s particularly exciting is how these systems learn from each procedure, continuously improving their assistance capabilities. Every surgery becomes a data point that makes the next one potentially better.
Personalized Treatment: The field of pharmacogenetics—studying how genetic variations affect drug responses—is being revolutionized by AI. By analyzing a patient’s genetic markers, AI can predict with remarkable accuracy whether a patient will respond well to a specific medication, what side effects might occur, and what dosage adjustments might be necessary. This is precision medicine in action—moving beyond one-size-fits-all treatments to therapies tailored to individual genetic profiles.
The implications are profound: fewer adverse drug reactions, improved treatment efficacy, and optimized therapeutic outcomes. We’re transitioning from medicine by trial-and-error to medicine by prediction and precision.
Healthcare Management and Public Health: Optimizing the System
Administrative Optimization: Hospitals generate enormous amounts of administrative and clinical data. AI systems can automate medical record management, optimize appointment scheduling, predict patient flow in emergency departments, and allocate resources more efficiently. This translates into reduced waiting times, better resource utilization, and healthcare workers who can focus more on patient care rather than administrative tasks.
Drug Discovery and Clinical Research: Traditional drug development is a decade-long, billion-dollar gamble with high failure rates. AI is accelerating this process by analyzing massive molecular databases to identify potential drug candidates, predicting their efficacy and safety profiles, and optimizing clinical trial designs. Machine learning can also analyze clinical trial results faster and more comprehensively than traditional methods, potentially reducing the time and cost of bringing new treatments to market.
Epidemic Prediction and Public Health: By analyzing anonymized data including population movements, online symptom reporting, and environmental factors, AI can predict disease outbreaks like influenza or COVID-19. These predictive models enable public health authorities to take proactive measures, allocate resources more effectively, and prepare healthcare systems for incoming patient surges. The COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated both the potential and the limitations of these systems—they’re powerful tools, but they’re only as good as the data they receive and the speed at which authorities act on their predictions.
The Dark Side of Medical AI: Confronting Uncomfortable Truths
AI in healthcare isn’t all breakthrough and celebration. Like any powerful technology, it carries risks that we must address head-on rather than sweep under the rug of enthusiasm.
Algorithmic Bias: The Digital Reflection of Human Prejudices
AI systems are only as good as the data used to train them, and healthcare data historically reflects the biases and inequalities of medical practice. If an AI system is trained primarily on data from white, male patients, it may be less accurate when diagnosing diseases in women or ethnic minorities. These algorithmic biases don’t just perpetuate existing health disparities—they can amplify them.
The solution isn’t to abandon AI but to be ruthlessly vigilant about data diversity and model auditing. We need diverse training datasets, regular bias testing, and transparency in AI decision-making processes. The stakes are too high to get this wrong.
Ethical and Legal Minefields
Responsibility and Accountability: When an AI system misses a diagnosis or recommends an inappropriate treatment, who bears responsibility? The software manufacturer, the hospital that purchased the system, or the physician who acted on its recommendation? Our legal frameworks haven’t caught up with technological reality, creating a gray area that could undermine patient trust and physician confidence.
Privacy and Data Security: AI requires massive datasets to function effectively, making patient data protection more critical than ever. Regulations like GDPR in Europe provide important frameworks, but the tension between data utility and privacy protection remains unresolved. Healthcare data is among the most sensitive information we possess—we need bulletproof security measures and transparent data use policies.
The Human Element: Perhaps the most significant risk is that AI could create distance between physicians and patients. Technology should enhance the human connection in healthcare, not replace it. AI should free up physicians to spend more time on empathy, listening, and emotional support—the irreplaceable human elements of healing.
The Future of AI in Healthcare: Augmented Medicine, Not Automated Medicine
The trajectory is clear: AI integration in healthcare will deepen, not diminish. But the future isn’t about robot doctors—it’s about augmented physicians with superhuman capabilities.
Connected Health and Telemedicine Revolution
AI will be seamlessly integrated into wearable devices and health sensors, continuously monitoring our health status, detecting anomalies, and alerting healthcare providers when intervention is needed. This constant health surveillance might sound dystopian, but it represents a shift from reactive to proactive healthcare—treating problems before they become serious.
Telemedicine, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, will become more sophisticated as AI analyzes patient data before consultations, enabling more accurate remote diagnoses and personalized treatment recommendations. The result could be healthcare that’s more accessible, especially for underserved populations.
The Rise of Preventive Medicine
By analyzing lifestyle data, genetic information, and environmental factors, AI will provide ultra-personalized recommendations for disease prevention. We’re moving from a healthcare system that treats illness to one that prevents it. Imagine receiving specific, evidence-based recommendations about diet, exercise, and lifestyle modifications based on your unique genetic profile and real-time health data.
This shift could fundamentally alter healthcare economics—preventing disease is far less expensive than treating it. But it also raises questions about health equity and access to these personalized prevention tools.
Training the Next Generation
For this AI-augmented future to succeed, medical education must evolve. Tomorrow’s physicians need to understand how to work with AI tools, interpret their outputs, and maintain critical thinking skills when AI recommendations don’t make sense. Medical schools are beginning to integrate AI literacy into their curricula, but the pace of change needs to accelerate.
The goal isn’t to create physicians who are dependent on AI, but professionals who can leverage these tools to provide better, faster, and more personalized care.
The Bottom Line: Embrace the Revolution or Be Left Behind
Artificial intelligence in healthcare isn’t a distant future—it’s the present reality. The question isn’t whether AI will transform medicine, but how quickly and how well we adapt to that transformation.
For healthcare professionals, this means embracing AI as a powerful ally rather than viewing it as a threat. For patients, it means becoming informed consumers who understand both the potential and limitations of AI-assisted healthcare. For policymakers, it means creating regulatory frameworks that promote innovation while protecting patients and ensuring equitable access.
The medical profession has survived and thrived through countless technological revolutions—from the stethoscope to antibiotics to medical imaging. AI represents the next chapter in this story of continuous improvement and innovation.
But here’s what makes this revolution different: its speed and scope. AI isn’t just improving one aspect of healthcare—it’s transforming diagnosis, treatment, surgery, drug development, and health management simultaneously. The physicians and healthcare systems that embrace this change will provide better care and achieve better outcomes. Those that resist will find themselves increasingly irrelevant.
The choice is ours, but the window for making that choice is narrowing. The AI revolution in healthcare is here. The only question is whether we’ll lead it or let it leave us behind.
Sources:
- American Medical Association & American College of Radiology: AI in Medicine Basics
- The Lancet Digital Health: Potential for AI in Healthcare
- Nature: Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks
- Journal of the National Cancer Institute: AI breast cancer detection studies
- Stanford University School of Medicine: AI skin cancer research
- World Health Organization: Ethics and governance of AI for health
Keywords: artificial intelligence medicine, medical AI applications, machine learning healthcare, deep learning diagnosis, AI medical imaging, robot surgery, personalized treatment AI, healthcare automation, medical AI ethics, AI diagnosis accuracy, healthcare technology revolution
Disclaimer: This educational content was developed with AI assistance by a physician. It is intended for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance. The information provided is valid as of the date indicated at the end of the article.

Comments